Sperm production: Where is sperm produced?
Follows NC° Editorial Policy
At Natural Cycles, our mission is to empower you with the knowledge you need to take charge of your health. At Cycle Matters, we create fact-checked, expert-written content that tackles these topics in a compassionate and accessible way. Read more...
Key Takeaways
- Sperm production takes place in the testicles and is regulated by hormones, such as testosterone
- It takes around two months for new sperm cells to be produced, and this is a continual process
- Sperm quality is an important factor in male fertility, alongside sperm count, and there are a few lifestyle changes you can make to support this
What is sperm?
Sperm or spermatozoa are a type of gamete or sex cell that’s essential for reproduction. [1] Sperm cells are some of the smallest cells in the human body and they are extremely high in numbers, with millions of sperm present in a single ejaculation.
Sperm may be small, but they’re pretty resilient. Sperm cells can survive in the female reproductive system for as many as five days. However, outside the body, they will deteriorate much faster and can only survive for a few minutes.
In all mammals, including humans, male sperm cells play an essential role in reproduction, together with the female egg cell. A male sperm cell is equipped for swimming, with a streamlined head, body (also called mid-piece), and tail. Each sperm cell looks a little bit like a tadpole. If sperm is ejaculated into the vagina, it travels through the female reproductive tract, where it may fertilize a female egg cell (the other type of gamete). Even though there are millions of sperm in each ejaculation, only one single sperm cell can fertilize the egg.
Sperm vs semen
Did you know that semen and sperm aren’t actually the same thing? Semen does contain sperm, but it also contains another liquid known as ‘seminal fluid.’ Semen is also another word for ejaculate or cum.
The sperm in semen comes from the testicles, but the seminal fluid is produced in other organs, including the prostate. The two are combined during ejaculation, and voila, that’s how semen is made! When it comes to male reproductive health, there’s plenty of ground to cover, so in this article, we’ll focus more on sperm production, also known as spermatogenesis.
How is sperm made?
The testicles are key to sperm production. While they appear from the outside to be round or ball-shaped, they are actually made up of tightly coiled small tubes (known as tubules). It’s within the walls of these tubules that the sperm cells are produced and then matured.
As with all things to do with reproductive health, hormones are hard at work when it comes to regulating sperm production and male fertility more broadly. The well-known male sex hormone, testosterone, is essential for sperm production. However, follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH) are also important, and both hormones are needed for the optimal development of the testicles and maximum sperm production. [2]
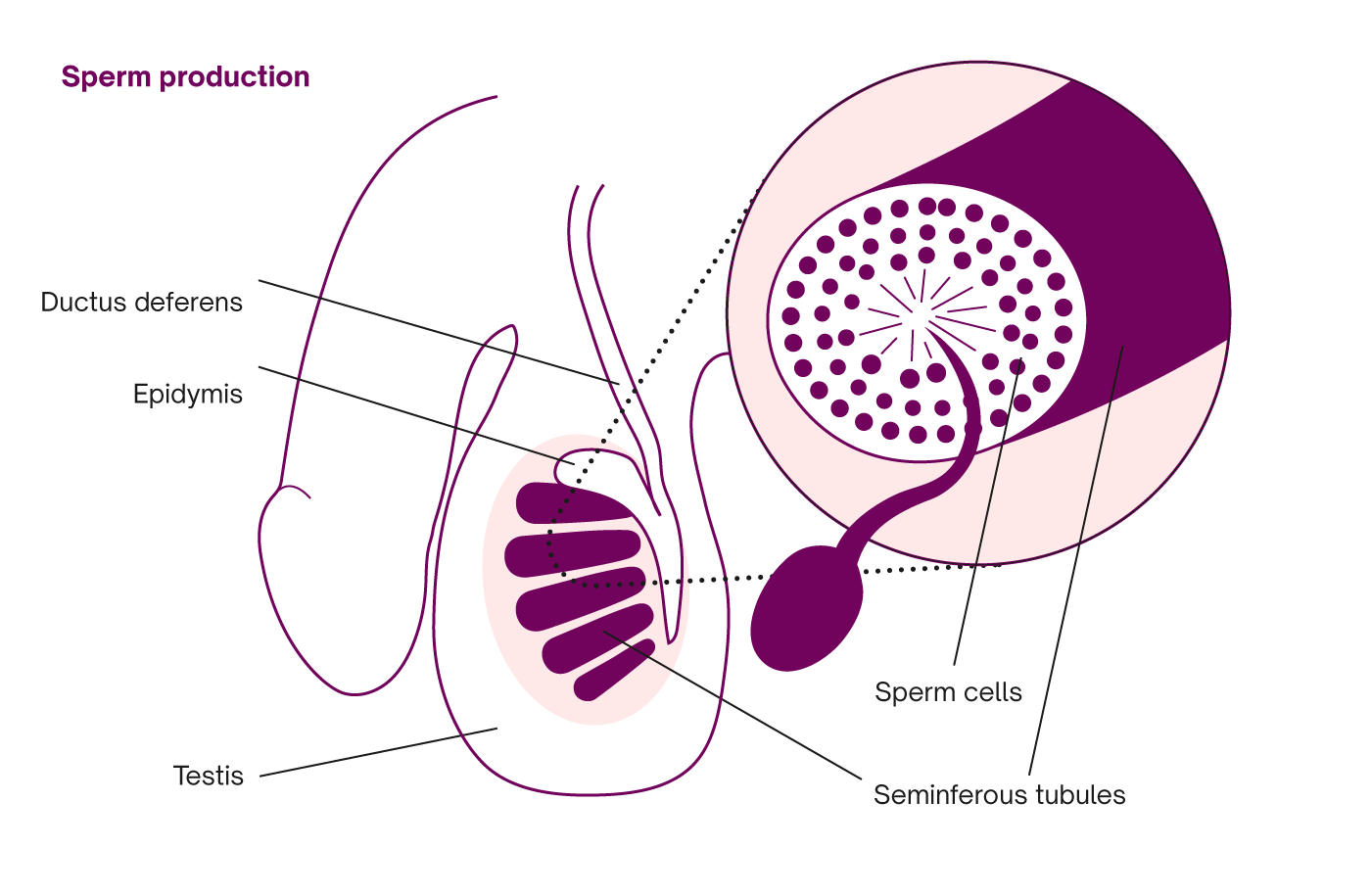
The process of sperm production
Sperm cell production takes around 70 days, but this varies between individuals. [3] Immature sperm cells will divide multiple times within the testes resulting in the production of the tadpole-like cells we recognize as sperm.
Sperm cells are primarily made up of water and plasma (a type of liquid base that’s common in cells of the human body). These sperm cells consist of a head, midpiece, and tail. The head contains the male’s genetic information, while the midpiece produces energy for swimming, and the tail enables swimming once the sperm has matured and is ejaculated.
In the final phase of sperm production, the sperm passes into the epididymis near the top of the testicles. The epididymis acts as a sort of holding bay, where the sperm can continue to mature and gain the ability to swim. It’s here that they are also fine-tuned for their potential future meeting with the female egg cell.

How many sperm cells does a man have?
Sperm counts will vary between individuals, but on average, there are around 80 million to 300 million sperm cells per ejaculation. [4] While sperm count plays an important role in male fertility, it is not the only factor. Sperm quality is important too. This often comes down to sperm motility (the ability of that sperm cell to swim), but there are other things that can reduce sperm quality, too, such as damaged or incomplete DNA.
How to improve sperm quality?
Remember that just like the varying patterns of the female menstrual cycle, semen quality in men is individualized and may change from month to month. It is quite normal for the quality of one male's ejaculate to increase and decrease over time, but maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle will help set good foundations for sperm production. [5]
Here are a few things you can keep in mind if you want to promote healthy sperm production:
- Drink less alcohol: Leading a healthy lifestyle is key to looking after all parts of our bodies, not just our reproductive health. Try to limit alcohol intake where possible.
- Eat healthily where possible: A diet that’s naturally rich in nutrients will also support a healthy body and sperm production in tandem. There is a growing body of research that shows male fertility can be impacted by being overweight or obese. [6] Eating a healthy diet can help combat this too. Choosing healthy foods is often easier said than done, but it’s worth keeping in mind if you’re concerned about sperm quality.
- Get plenty of exercise: Making time for regular workouts is an important part of maintaining a healthy weight and can support your overall health and well-being, which in turn is linked to your fertility.
- Stop smoking: Tobacco products have been shown to have a direct link to male infertility .[7] It’s a good idea to cut down or stop smoking altogether if you are looking to improve your sperm count, quality, and general health.
- Avoid recreational drugs: Anabolic steroids are often used to gain muscle mass, but these can have a negative impact on male fertility. [8] The same goes for other substances like cocaine. [9] As part of a healthy lifestyle, it’s important to cut out recreational drugs, and this may also support future fertility.
- Keep your testes cool: Overheating the testicles can reduce sperm count, so it’s important to keep your nether regions cool and comfortable by opting for loose-fitting underwear.
- Wait a couple of months: It’s important to remember that the process of sperm production takes several months to complete. That means if you make lifestyle changes today, it will take a little while before you see results. Otherwise, healthy individuals who experience an infection or are unwell for a short period of time may also see a temporary drop in fertility for a couple of months after infection.[10]
Is male fertility affected by age?
It’s well-known that female fertility decreases as we get older, but what about male fertility? While it’s not as clear cut, there’s evidence to suggest that the likelihood of conceiving is also affected by a man’s age and that sperm concentration, motility, and quality all decrease with age. [11] It’s also shown that erectile dysfunction (ED) increases with age, and this can also lead to difficulty conceiving. [12]
Keep in mind that fertility issues may also be affected by older men also tending to have older female partners, and not all research has accounted for the age of the woman in the relationship. While it’s certainly possible to have a healthy and plentiful sperm count well into later life, age is one more factor you might want to think about if you’re interested in planning pregnancy.
When to talk to your doctor about sperm health
If you are worried about your fertility or have questions about your sperm quantity or quality, you can talk to a healthcare professional for advice. If you’re trying to conceive, it’s usually recommended you try for 12 months before talking to your doctor. However, this will depend on other factors, such as you and your partner’s age and health history.
When you visit your doctor, you may be asked to provide a sample of your semen. This will be analyzed to determine how healthy and plentiful your sperm count is. While having a low sperm count can be worrying, remember it only takes one healthy sperm cell to fertilize an egg. Through techniques like IVF, medical professionals can select sperm cells and increase the chances of fertilization.
Everyone’s fertility journey is different
It’s important to highlight that everyone’s route to conceiving looks a little different. There are many factors at play when it comes to our fertility, and sperm health is just one of them. Female fertility plays a huge role in conception too, and that’s where Natural Cycles can help.
Get pregnant faster with Natural Cycles
A certified app that’s based on body temperature, Natural Cycles is able to pinpoint fertile days within the menstrual cycle, so you know the best days to have sex to increase your chances of conception. Research shows that couples who used Natural Cycles to get pregnant did so in three cycles on average.[13]
With NC° Partner View, you can share the responsibility of planning or preventing pregnancy. This feature is designed so you can view your partner’s fertile window and learn more about reproductive health along the way. Ready to plan a pregnancy and learn more about your body? Why not find out if Natural Cycles could work for you?
Did you enjoy reading this article?