Sexually transmitted infections: STDs vs STIs, symptoms, & treatment
Follows NC° Editorial Policy
At Natural Cycles, our mission is to empower you with the knowledge you need to take charge of your health. At Cycle Matters, we create fact-checked, expert-written content that tackles these topics in a compassionate and accessible way. Read more...
Key Takeaways
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites transferred from one person to another via sexual contact
- Although they may be asymptomatic, common STI symptoms include inflammation or itchiness in the genital area, abdominal pain, abnormal odor or discharge, sores, and more, depending on the specific STI
- Regular testing and methods of prevention are key to managing the spread of STIs and reducing your risk of more serious medical complications
- Talk to your healthcare provider as soon as you notice any potential STI symptoms, or if you suspect that you’ve been exposed to an STI
On this page
- What is a sexually transmitted infection?
- What are the types of sexually transmitted infections?
- What are the symptoms of sexually transmitted infections?
- What causes sexually transmitted infections?
- How are sexually transmitted infections diagnosed?
- What to do if you have an STI
- When to speak with a doctor
- Get to know your body better with Natural Cycles
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are conditions passed from person to person via sexual contact. The topic of STIs can be sensitive and serious — even uncomfortable — but it’s important to have open and honest conversations about them for the sake of your health and the health of those you care about.
They’re relatively common, although they vary in severity. In fact, it’s estimated that about 80% of sexually active adults in the United States will get human papillomavirus (HPV) at some point [1]. Some can be easily treated while others may have lasting effects that lead to serious health problems down the line. Symptoms vary as well — some have very severe, noticeable symptoms while others may be completely asymptomatic but still cause negative health effects.
In this article, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about STIs, including types, symptoms, causes, treatment, and how to lower your risk of contracting STIs.
What is a sexually transmitted infection?
An STI is an infection that is passed from one person to another through oral, vaginal, or anal sexual contact. They can affect all sexually active people regardless of age, gender, or sexual orientation, but women tend to be at higher risk of complications from STIs. The good news is that these infections can also be prevented effectively with proper screening and education [1].
STD vs STI
You may have heard the terms “STDs” and “STIs” used interchangeably in the past. STD stands for “sexually transmitted disease,” while STI stands for “sexually transmitted infection.” There’s a slight (but important) difference between the two [2].
An STI enters the body via sexual contact. If this initial infection isn’t treated, it can then develop into a disease (an STD). This means that not all STIs will result in disease. STDs usually come with more prominent symptoms and potential health complications. This is why screening and treatment for STIs is essential for your sexual health — the sooner you catch and treat them, the better [2].
What are the types of sexually transmitted infections?
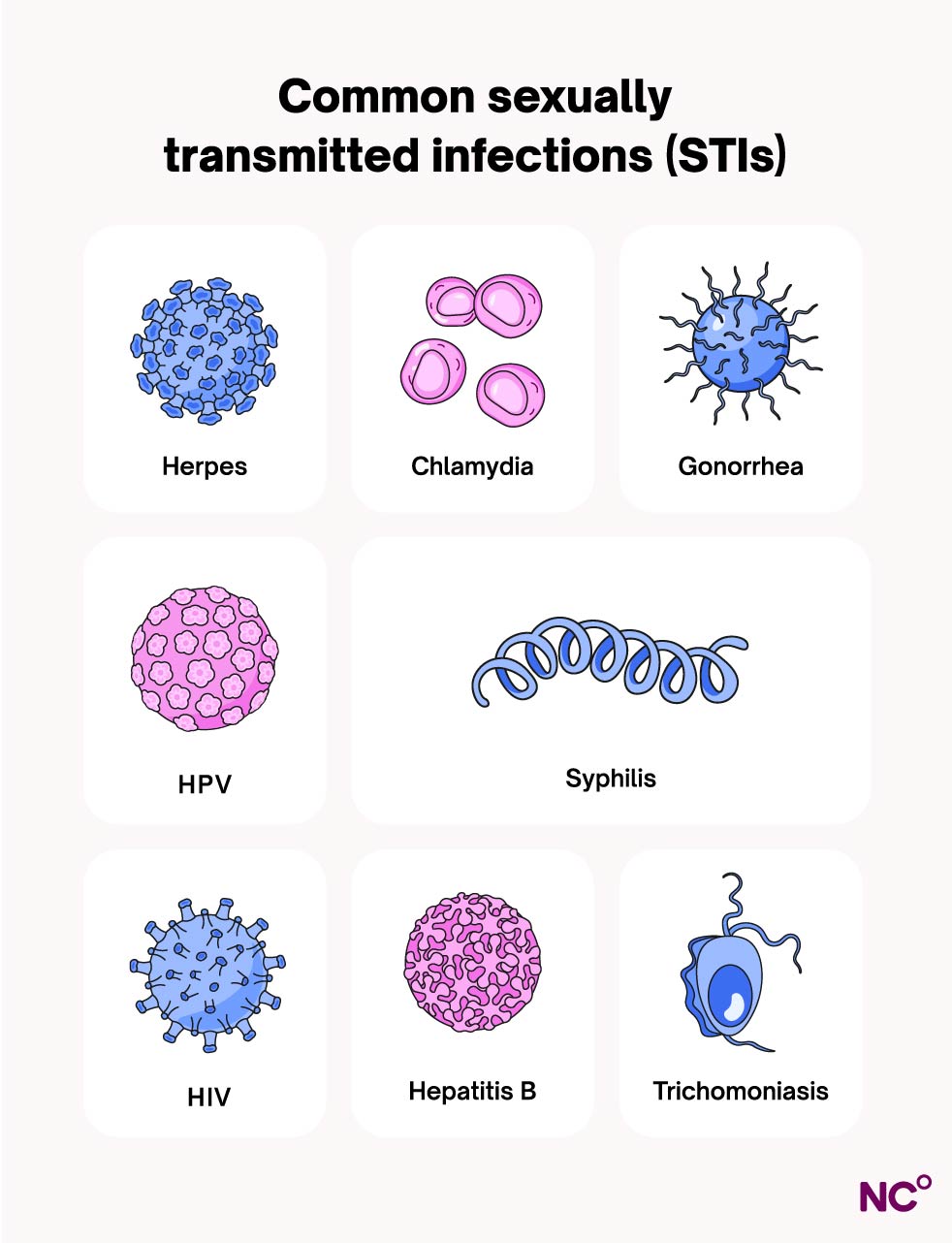
There are over 20 types of STIs, and most of them are curable. Some of the most common of these include:
- Chlamydia: This STI tends to be present without symptoms, but if there are symptoms, these may include abnormal vaginal discharge or bleeding, along with lower pelvic pain and frequent urination.
- Gonorrhea: This involves inflammation of the genital area, along with urinary frequency/urgency, lower pelvic pain, and abnormal vaginal bleeding.
- Syphilis: May be asymptomatic (without symptoms), but syphilis can manifest as painless lesions, an ulcer, or rashes on the genitals. They can appear months or even years after infection.
- Trichomoniasis: Usually characterized by itching in the genital area, foul-smelling green discharge, pain during sex, and/or spotting [1]
Other types of STIs aren’t necessarily curable, but their symptoms can be treated effectively with proper medication. These include:
- Genital herpes: Commonly involves painful, itchy sores in the genital area or on the mouth. It can also cause fever, headaches, and pain during urination.
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): May be asymptomatic, but this STI can cause fever, chills, fatigue, and body aches and pains.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV): Also typically asymptomatic, but can cause genital warts and cervical cancer [1].
The most commonly reported STI worldwide is HPV. At any given time, it’s estimated that about 80% of sexually active people have HPV, including 42% of adults ages 18 to 59. In fact, the Center for Disease Control estimates that almost every sexually active person who is not vaccinated against HPV will contract it at some point in their lives [1]. Professional medical societies like the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommend that everyone get vaccinated for HPV in early adolescence [3].
In terms of curable STIs, trichomoniasis is the most commonly reported, with 156 million new cases yearly. Chlamydia is next at 127 million, then gonorrhea at 87 million, and finally syphilis at 6.3 million new cases reported annually [1]. The prevalence of STIs is concerning for public health reasons, but reducing the social stigma around these conditions can lead to more effective preventative measures and treatments.
What are the symptoms of sexually transmitted infections?
STIs don't always cause symptoms, and sometimes the symptoms are very mild. Symptoms may even be mistaken for another condition as well, like a urinary tract infection (UTI) or a yeast infection [4]. Asymptomatic STIs can still be spread via sexual contact without even knowing that you have the infection [5].
If you are experiencing STI symptoms, they may include:
- Abdominal pain
- Abnormal vaginal odor
- Anal itching, soreness, or bleeding
- Blisters or sores in or around the mouth
- Fever
- Itching and redness in the genital area
- Painful or frequent urination
- Sores or warts on the genital area
- Unusual discharge [x]
What can I expect if I have a sexually transmitted infection?
You may not notice anything if you’ve contracted an STI since many may not cause symptoms. But depending on your situation, you may experience some of the STI symptoms outlined above. It’s best to talk to your healthcare provider as soon as you notice something out of the ordinary so that they can test for the root cause and treat it quickly.
What causes sexually transmitted infections?
STIs are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites that enter the body via genital and/or skin-to-skin contact during sex. These microorganisms invade healthy cells in the body and spread, resulting in an infection, and potentially causing the STI symptoms mentioned above [5].
Are sexually transmitted infections contagious?
Yes, they’re very contagious. Person-to-person contact is the main way that these infections spread, but they don’t all necessarily require sexual contact or even intercourse. It’s important to know that different STIs can be passed along in different ways, so it’s always a good idea to practice safe sex by using barrier birth control methods and having open, honest conversations with your partner(s).
For example, if you or your partner has an incurable STI like HPV, HSV, or HIV, there are measures you can both take to decrease your chances of spreading them, such as PreP or valtrex medications, barrier methods of birth control, and avoiding anal sex. Talk to your healthcare provider to get more details about the best ways to prevent STIs.
How are sexually transmitted infections spread from person to person?
Most STIs are spread through vaginal, oral, or anal sex, but some (like herpes and HPV) can also be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact or oral sex, even without intercourse. Certain STIs can be passed from mother to fetus during pregnancy, childbirth, or while breastfeeding (safe treatment options are available for pregnant people who contract STIs). Blood transfusions or sharing needles can also spread STIs [5].
How are sexually transmitted infections diagnosed?
STI testing and diagnosis can be done by your healthcare provider or at a sexual health clinic. You can get tested for multiple STIs at once with different screening methods, but if you have questions or concerns about a specific STI, check with your healthcare provider to make sure it’s included in the screening or if it needs a separate follow up appointment [5].
Testing methods for STIs usually include:
- A physical pelvic exam to look for signs of infection.
- Getting blood drawn and sending that blood to a lab for STI testing.
- A urine test that will also be evaluated in a lab.
- A pap smear can identify HPV and trichomonas.
- Fluid or tissue samples taken with a cotton swab from the potentially infected area of the body. This fluid is examined under a microscope in a lab to look for signs of STIs [4].
How often should I get tested for STIs?
Because they can be asymptomatic, it’s important to get regular screenings for STIs, especially if you have new or multiple sexual partners. It’s also recommended to watch out for signs of new, active infections like tingling in the genital area, and avoiding intercourse if you notice that something is off. Talk to your healthcare provider to assess your risk level and get recommendations on how often you should be tested. The testing you need and how often you may need them depends on your unique circumstances.
While it may be an uncomfortable conversation at first, remember that doctors are specialists who have these types of conversations every day. Having a frank and honest conversation can help your provider see the full picture and get you the information and care you need. Furthermore, making STI screening a routine part of your medical check-up can destigmatize the process, make treatment easier, and prevent further diseases and complications for you and your partner(s) [4, 5].
What to do if you have an STI
If you’ve been diagnosed with an STI, your healthcare provider will go over next steps for treatment with you. This usually involves taking a prescribed oral medication (an antibiotic or an antiviral) [5].
If you suspect that you’ve contracted an STI, it’s a good idea to see a healthcare professional quickly. If left untreated, some STIs can lead to more serious complications and long term health impacts, so the sooner you address them with your healthcare provider, the better. When you start treatment, talk to your provider about how long to wait to have sex again to avoid passing the infection along, increasing the chance for re-infection in the future [4, 5].
How soon after treatment will I feel better?
This depends on the STI and the severity of symptoms, and your healthcare provider can give you more details about what to expect with STI treatment, but here are a few examples of the treatment timelines of common STIs:
- Gonorrhea: Symptoms often subside in about four days, and about 90% of people see symptoms resolved within a week of starting treatment [6].
- Herpes: The initial outbreak can last up to four weeks without treatments, but recurrent outbreaks are shorter (about five to 10 days) if antiviral treatments are taken [7].
- Trichomoniasis: Most people find that their symptoms clear up in about one week after starting treatment [8].
How to lower my risk of STIs
The best way to protect against STIs is to practice safe sex, using barrier birth control methods like the condom or the dental dam, or to abstain from unprotected sex. Regular STI screenings and pap smears for you and your partner(s) are a great way to stay on top of your reproductive health as well. It’s also recommended to get a sexual health check up after having unprotected sex with a new partner and/or if you’re having unprotected sex regularly. As we mentioned earlier, vaccines are available to protect against both HPV and hepatitis B and are highly recommended by the ACOG [4].
Avoid douching, as this type of cleaning can make it difficult for “good” bacteria to survive in the vagina. Additionally, douching has not been proven to prevent STIs. In fact, some of the chemicals in douches can increase the likelihood of contracting STIs. Spermicides also increase the risk of STIs as they can irritate the vaginal canal, so you may want to consider avoiding those as well [4].
None of these recommendations alone can completely protect you against STIs, and they’re most effective when used together. Your healthcare provider can provide the best recommendations for your unique circumstances in terms of preventing STIs [4].
When to speak with a doctor
As we’ve mentioned throughout this article, speak with a healthcare provider as soon as you notice something out of the ordinary that may be an STI symptom, or if you suspect that you’ve been exposed to an STI. Early testing and treatment is key for dealing with these infections and preventing disease. With swift medical attention and treatment, you can avoid these challenges and take charge of your sexual health [1].
Get to know your body better with Natural Cycles
Discover more ways to look after your reproductive health with Natural Cycles. With support from our Cycle Matters library of carefully curated health topics, to support in your reproductive journey with modes like NC° Birth Control and beyond, the Natural Cycles app can help you have informed and productive conversations with your healthcare provider about your sexual health. See if Natural Cycles can work for you today.
Did you enjoy reading this article?